Chapter 1: Introduction to UI/UX Design
1.1 Introduction
In today's digital age, where websites, mobile applications, and software products play a crucial role in everyday life, the importance of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design cannot be overstated. These two disciplines are fundamental in shaping how users interact with digital products, influencing their satisfaction, engagement, and overall usability.
UI/UX design is a multidisciplinary field that blends psychology, design principles, technology, and business strategy to create intuitive and effective user interactions. While UI focuses on the visual aspects and interactive elements of a product, UX ensures that the product delivers a seamless, accessible, and enjoyable experience for users. This chapter introduces the key concepts of UI/UX design, explaining their roles, significance, and the principles that guide the creation of user-friendly digital products.
1.2 What is User Experience (UX) Design?
1.2.1 Definition of UX Design
User Experience (UX) design refers to the process of designing products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. It encompasses all aspects of a user's interaction with a company, its services, and its products. The goal of UX design is to enhance user satisfaction by improving usability, accessibility, and overall interaction quality.
A well-designed UX ensures that users can efficiently accomplish their goals while enjoying a smooth and intuitive interaction. Poor UX design, on the other hand, can lead to frustration, decreased user engagement, and even loss of customers.
1.2.2 Key Components of UX Design
UX design is a broad discipline that includes several essential components:
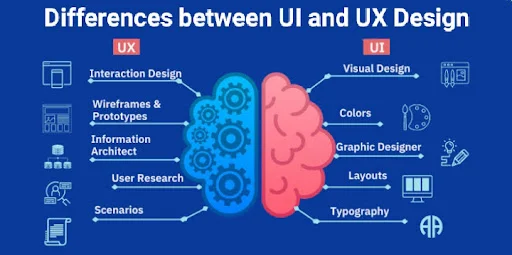
- User Research – Understanding the target audience, their needs, preferences, and pain points through surveys, interviews, and data analysis.
- Information Architecture (IA) – Structuring content and navigation in a way that makes it easy for users to find what they need.
- Wireframing & Prototyping – Creating low-fidelity and high-fidelity sketches or models of a product to visualize its structure and flow before development.
- Interaction Design – Designing how users interact with the product, including animations, transitions, and interactive elements.
- Usability Testing – Conducting tests with real users to identify usability issues and improve the design based on feedback.
1.3 The Role of User Interface (UI) Design
1.3.1 Definition of UI Design
User Interface (UI) design focuses on the visual and interactive aspects of a digital product. It involves designing the layout, colors, typography, buttons, icons, and other elements that users interact with. UI design aims to create an aesthetically pleasing and functional interface that aligns with the overall UX design principles.
1.3.2 Responsibilities of a UI Designer
A UI designer is responsible for:
- Visual Design – Creating the look and feel of the product, including branding, color schemes, and typography.
- Layout Design – Arranging elements in a way that enhances usability and ensures a smooth user flow.
- Interactive Elements – Designing buttons, icons, sliders, and other interactive components that users engage with.
- Consistency in Design – Ensuring that the design elements are uniform across different screens and devices for a cohesive experience.
1.3.3 Differences Between UI and UX Design
Although UI and UX are closely related, they have distinct roles:
| Feature | UX Design | UI Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | User experience and interaction | Visual elements and aesthetics |
| Goal | Improve usability and user satisfaction | Enhance the visual appeal and engagement |
| Process | Research, wireframing, usability testing | Layout design, typography, colors |
| Outcome | A seamless and intuitive experience | A visually appealing and interactive interface |
Both UI and UX must work together to create a product that is not only beautiful but also functional and user-friendly.
1.4 Key Principles of Good UI/UX Design
Effective UI/UX design is based on several key principles that ensure a product is usable, accessible, and enjoyable.
1.4.1 Usability
Usability refers to how easily users can interact with a product and achieve their goals. A highly usable product should be:
- Intuitive: Users should not need extensive instructions to use the interface.
- Efficient: Tasks should be completed quickly and without unnecessary steps.
- Error-Free: The design should minimize errors and provide easy ways to correct mistakes.
1.4.2 Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that digital products can be used by people with different abilities, including those with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. Key accessibility considerations include:
- Providing alternative text for images for visually impaired users.
- Ensuring keyboard navigation for users who cannot use a mouse.
- Using high-contrast text for readability.
1.4.3 Consistency
Consistency in UI/UX design means maintaining uniformity in visual elements, layouts, and interaction patterns. This helps users:
- Learn and adapt to the interface quickly.
- Predict how different parts of the product will behave.
- Experience a seamless transition between different sections or devices.
1.4.4 Feedback and Responsiveness
Providing feedback helps users understand the system's response to their actions. This includes:
- Visual cues (e.g., button changes color when clicked).
- Error messages that clearly explain issues.
- Loading indicators to show progress.
1.4.5 Mobile-Friendly Design
With a significant number of users accessing digital products on mobile devices, ensuring responsive design is crucial. A mobile-friendly design:
- Adjusts layouts to fit different screen sizes.
- Uses touch-friendly buttons and interactions.
- Ensures fast loading times for mobile users.
1.5 Conclusion
UI/UX design plays a vital role in shaping how users interact with digital products. While UX design focuses on the overall experience, UI design ensures a visually appealing and interactive interface. The success of any digital product depends on its usability, accessibility, consistency, and responsiveness. By following key design principles, designers can create products that are not only functional but also engaging and delightful for users.
This chapter provided a foundational understanding of UI/UX design, setting the stage for deeper exploration into design processes, tools, and best practices in the subsequent chapters.
Comments
Post a Comment
"Thank you for seeking advice on your career journey! Our team is dedicated to providing personalized guidance on education and success. Please share your specific questions or concerns, and we'll assist you in navigating the path to a fulfilling and successful career."