Chapter 18: Implementation and Case Studies: Implementing a Quality Management System (QMS)
- Planning and Preparation:
- Define Quality Policy: Establish a clear vision for quality aligned with organizational goals.
- Identify Relevant Processes: Map out key business processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Set Quality Objectives: Define measurable targets related to quality performance.
- Allocate Roles and Responsibilities: Assign ownership for quality initiatives across different departments.
- Define Quality Policy: Establish a clear vision for quality aligned with organizational goals.
- Implementation:
- Develop Procedures and Documentation: Create detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) for each key process.
- Training and Awareness: Educate employees on quality standards, procedures, and relevant tools.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Establish metrics and monitoring systems to track performance against objectives.
- Process Improvement: Utilize quality tools like root cause analysis to identify and address process issues.
- Develop Procedures and Documentation: Create detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) for each key process.
- Monitoring and Continuous Improvement:
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Management Review: Regularly review quality performance data and identify areas for further improvement.
- Corrective Action: Implement corrective actions to address identified non-conformances.
- Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Manufacturing Company:A large automotive manufacturer implemented a QMS to reduce production defects and improve customer satisfaction by standardizing manufacturing processes, utilizing statistical process control (SPC), and training operators on quality standards.
- Healthcare Provider:A hospital deployed a QMói8iS to enhance patient safety and reduce medical errors by implementing standardized procedures for medication administration, infection control protocols, and thorough documentation practices.
- Software Development Company:A software development firm used a QMS to improve software quality by incorporating rigorous testing methodologies, code reviews, and defect tracking systems throughout the development lifecycle.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Consistent quality in products and services leads to higher customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizing errors and rework can significantly decrease operational costs.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes and improved communication can lead to increased productivity.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to industry standards and regulations can mitigate legal risks.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: A QMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement across the organization.
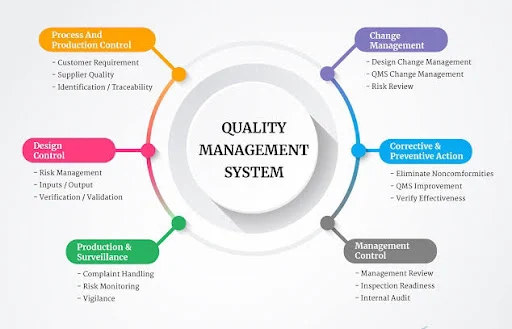
18.1 Introduction
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a structured framework designed to ensure that an organization consistently meets customer requirements and regulatory standards. Implementing a QMS involves a systematic approach that includes planning, documentation, training, monitoring, and continuous improvement. This chapter discusses the step-by-step process of QMS implementation and presents case studies illustrating successful implementations across different industries.
18.2 Steps for Implementing a QMS
18.2.1 Define Quality Objectives and Scope
The first step in implementing a QMS is to define the quality objectives aligned with the organization’s vision and mission. The scope of the QMS should be determined, identifying the processes, departments, and products/services covered.
18.2.2 Obtain Top Management Commitment
Successful QMS implementation requires the commitment of top management. Leadership should actively support the process, allocate necessary resources, and promote a quality culture within the organization.
18.2.3 Identify Key Processes and Responsibilities
Organizations should map their key processes and define responsibilities for quality management. A process approach should be adopted to ensure effective interactions between different business functions.
18.2.4 Develop Quality Policy and Documentation
A clear quality policy should be established to guide the QMS implementation. The organization must develop necessary documentation, such as:
- Quality Manual
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Work Instructions
- Records and Forms
18.2.5 Conduct Training and Awareness Programs
Employees at all levels should receive training on QMS principles, procedures, and their role in maintaining quality standards. Awareness programs help in fostering a culture of quality and continuous improvement.
18.2.6 Implement the QMS and Conduct Internal Audits
The organization should implement the documented QMS processes and conduct internal audits to assess compliance. Internal audits help identify gaps, non-conformities, and areas for improvement before external certification audits.
18.2.7 Monitor, Measure, and Improve
Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to monitor the effectiveness of the QMS. Continuous improvement tools such as PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), Six Sigma, and Lean methodologies can be used to enhance quality performance.
18.2.8 Obtain Certification (if applicable)
If the organization seeks certification (e.g., ISO 9001), a certification body should be engaged to conduct an external audit. Compliance with certification requirements validates the organization’s commitment to quality.
18.3 Challenges in QMS Implementation
Implementing a QMS may present several challenges, including:
- Resistance to change from employees
- Inadequate training and awareness
- Lack of top management support
- Complex documentation requirements
- Resource constraints
To overcome these challenges, organizations should ensure effective communication, provide adequate training, and adopt a phased approach to implementation.
18.4 Case Studies on QMS Implementation
18.4.1 Case Study 1: Implementing ISO 9001 in a Manufacturing Company
Background
XYZ Manufacturing Ltd., a mid-sized automotive parts manufacturer, aimed to implement ISO 9001 to improve product quality and customer satisfaction.
Implementation Steps
- Assessment and Planning – Conducted a gap analysis to identify areas needing improvement.
- Process Mapping – Defined and documented key processes such as procurement, production, and quality control.
- Training Programs – Provided QMS training for employees at all levels.
- Internal Audits – Conducted internal audits to ensure compliance before the certification audit.
- Continuous Improvement – Established corrective and preventive actions for identified non-conformities.
Results
- Achieved ISO 9001 certification within one year.
- Improved product quality and reduced defects by 20%.
- Increased customer satisfaction scores by 15%.
18.4.2 Case Study 2: QMS Implementation in a Healthcare Facility
Background
A multispecialty hospital aimed to enhance patient care and safety by implementing a QMS based on ISO 13485 (for medical devices) and ISO 9001.
Implementation Steps
- Leadership Commitment – Hospital management led the QMS initiative.
- Process Standardization – Standard operating procedures were developed for patient care, infection control, and equipment maintenance.
- Employee Training – Medical staff received training on quality and patient safety protocols.
- Performance Monitoring – Key performance indicators such as patient wait time and treatment effectiveness were tracked.
- External Audits – Engaged a certification body to validate compliance with ISO standards.
Results
- Reduced patient complaints by 30%.
- Improved operational efficiency and reduced medical errors.
- Enhanced compliance with healthcare regulations.
18.5 Conclusion
Implementing a QMS is a structured process that requires careful planning, strong leadership, employee involvement, and continuous monitoring. Organizations that successfully implement a QMS can achieve improved product/service quality, regulatory compliance, and enhanced customer satisfaction. The case studies presented demonstrate the practical benefits of QMS implementation across different sectors. By following best practices and overcoming challenges, organizations can build a sustainable quality culture and drive continuous improvement.
Comments
Post a Comment
"Thank you for seeking advice on your career journey! Our team is dedicated to providing personalized guidance on education and success. Please share your specific questions or concerns, and we'll assist you in navigating the path to a fulfilling and successful career."