How Accurate Economic Order Quantity (EoQ) Can Significantly Benefit an Industry? Being properly prepared is one of the biggest assets in business!!
Abstract
Economic order quantity (EOQ) concerns the most cost-efficient method of ordering stock. The objective is to find the order quantity that minimizes the total inventory holding costs and ordering costs.
Holding costs (otherwise known as carrying costs) are the costs to store the inventory and include the storage space, rent, deterioration, obsolescence, property tax, insurance, etc. Obviously, the more inventory ordered, the higher the holding costs will be.
Ordering costs are the costs that arise every time inventory is ordered. Ordering costs include the costs of creating a purchase order, processing an order, receiving and inspecting orders, etc. Note that the actual price of the items is not included in ordering costs. No matter what size the order is, ordering costs will be incurred with every order; the more orders placed, the higher the ordering costs will be.
What is EOQ?
EOQ stands for Economic Order Quantity. It is a measurement used in the field of Operations, Logistics, and Supply Management. In essence, EOQ is a tool used to determine the volume and frequency of orders required to satisfy a given level of demand while minimizing the cost per order.
The Importance of EOQ
The Economic Order Quantity is a set point designed to help companies minimize the cost of ordering and holding inventory. The cost of ordering inventory falls with the increase in ordering volume due to purchasing on economies of scale. However, as the size of inventory grows, the cost of holding the inventory rises. EOQ is the exact point that minimizes both of these inversely related costs.
This, Calculating EOQ can help companies and businesses reduce their expenses by balancing their inventory costs. When companies try to reduce expenses in one area of their inventory costs without EOQ, they can often increase the expenses in another area.
EOQ Formula
The Economic Order Quantity formula is calculated by minimizing the total cost per order by setting the first-order derivative to zero. The components of the formula that make up the total cost per order are the cost of holding inventory and the cost of ordering that inventory. The key notations in understanding the EOQ formula are as follows:
Components of the EOQ Formula:
D: Annual Quantity Demanded
Q: Volume per Order
S: Ordering Cost (Fixed Cost)
C: Unit Cost (Variable Cost)
H: Holding Cost (Variable Cost)
i: Carrying Cost (Interest Rate)
Definition and Formulas of EoQ
Ordering Cost
The number of orders that occur annually can be found by dividing the annual demand by the volume per order. The formula can be expressed as:

For each order with a fixed cost that is independent of the number of units, S, the annual ordering cost is found by multiplying the number of orders by this fixed cost. It is expressed as:
Holding Cost
Holding inventory often comes with its own costs. This cost can be in the form of direct costs incurred by financing the storage of said inventory or the opportunity cost of holding inventory instead of investing the money elsewhere. As such, the holding cost per unit is often expressed as the cost per unit multiplied by the interest rate, expressed as follows:
H = iC
With the assumption that demand is constant, the quantity of stock can be seen to be depleting at a constant rate over time. When inventory reaches zero, an order is placed and replenishes inventory as shown:
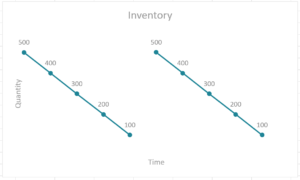
As such, the holding cost of the inventory is calculated by finding the sum product of the inventory at any instant and the holding cost per unit. It is expressed as follows:
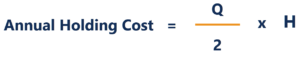
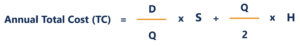
Total Cost and the Economic Order Quantity
Summing the two costs together gives the annual total cost of orders. To find the optimal quantity that minimizes this cost, the annual total cost is differentiated with respect to Q. It is shown as follows:
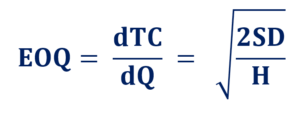
Example
For example, a company faces an annual demand of 2,000 units. It costs the company $1,000 for every order placed and $250 per unit of the product. It faces a carrying cost of 10% of a unit cost. What is the economic order quantity?
The variables can be arranged as follows:
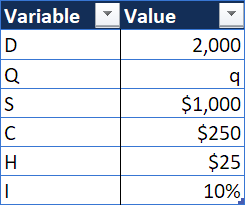
The cost for each value of Q is shown as:


Conclusions
Inventory optimization – that is, making sure your inventory is slimmed down to free up capital and increase margins while you still maintain high service levels – is how small- and mid-sized businesses can make their mark in their industry. But keeping track of all the considerations that go into inventory optimization requires constant analysis.
References
Materials and Logistics Management by L. C. Jhamb
Handbook Of Materials Management by Gopalkrishnan
Introduction To Materials Management reference book by Tony Arnold
Materials & Logistics Management reference book By Dr. Kasande
Materials Management: Procedures, Text & Cases by A. K. Datta
Purchasing & Materials Management by Gopalakrishnan
Materials and Logistics Management reference book by Saroj Kumar


Comments
Post a Comment
"Thank you for seeking advice on your career journey! Our team is dedicated to providing personalized guidance on education and success. Please share your specific questions or concerns, and we'll assist you in navigating the path to a fulfilling and successful career."