What's Renewable Energy? Learn It's Common Sources, Types, Benefits and Much More...
We can define renewable energy as those energies which can never be depleted. The importance of renewable energy is invaluable.
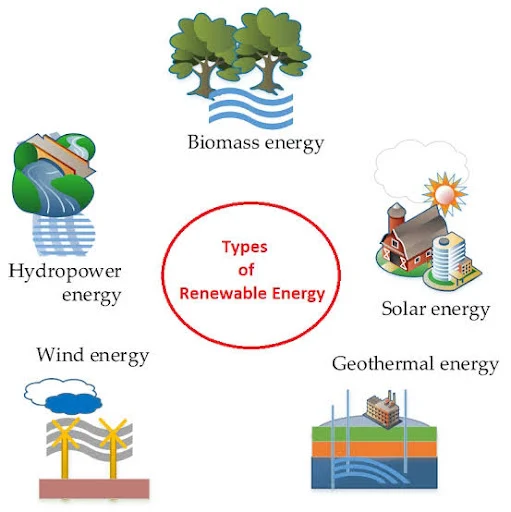
The sources are different from fossil fuels, such as oil, coal, and natural gas. Some examples of renewable energy sources are:
- Wind energy
- Solar energy
- Geothermal energy
- Hydropower
- Bioenergy
Geothermal energy is heat energy from the earth—Geo (earth) + thermal (heat).
Geothermal resources are reservoirs of hot water that exist or are human made at varying temperatures and depths below the earth's surface. Wells, ranging from a few feet to several miles deep, can be drilled into underground reservoirs to tap steam and very hot water that can be brought to the surface for use in a variety of applications.
Hydropower is the largest renewable energy source for electricity in the United States, though wind energy is soon expected to take over the lead. Hydropower relies on water—typically fast-moving water in a large river or rapidly descending water from a high point—and converts the force of that water into electricity by spinning a generator’s turbine blades.
Mega-dams divert and reduce natural flows, restricting access for animal and human populations that rely on those rivers. Small hydroelectric plants (an installed capacity below about 40 megawatts), carefully managed, do not tend to cause as much environmental damage, as they divert only a fraction of the flow.
10 advantages of renewable energy and underscores its significance in the years to come.
1. Environmental Benefits:
One of the most compelling advantages of renewable energy is its potential to positively impact the environment. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and gas, contributes around 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions. To tackle the threat of climate change, emissions need to be reduced by almost half by 2030. The importance of renewable resources in this context cannot be overstated.
2. Economic Growth:
The renewable energy importance in the economic sector is evident in its contribution to job creation and industry growth. As the demand for renewable energy increases, sectors related to its production and maintenance see a surge in job opportunities. This not only boosts the economy but also provides sustainable employment opportunities. Furthermore, the importance of renewable energy in stimulating local economies cannot be ignored.
Local projects often mean local jobs, ensuring that the benefits of renewable energy projects are felt directly within the community. According to IRENA, worldwide employment in the sector has escalated by nearly 700,000 from 2020-2021, reaching 12.7 million jobs.
3. Energy Independence:
The need for renewable energy stems from a desire for energy independence. Countries that rely heavily on imported fossil fuels are vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
By investing in renewable energy in future, nations can ensure a more stable, reliable, and independent energy supply, safeguarding their energy security.
4. Inexhaustible Energy:
The future of renewable energy looks promising, primarily because these sources are inexhaustible. While fossil fuels are finite and depleting, the sun, wind, and water are endless sources of energy.
This renewable energy is the future perspective that ensures that we have a continuous, unending supply of power. It underscores the importance of renewable energy as a long-term solution to the world’s energy needs.
Advancements:
The benefits of renewable energy are further amplified by rapid technological advancements. As research in this sector intensifies, we’re witnessing innovations that make renewable energy more efficient and accessible.
The energy sources of the future will be shaped by these technological leaps, ensuring that renewable energy becomes even more integral to our daily lives. The marriage of technology and renewable energy holds the promise of a brighter, cleaner future.
6. Reduction in Energy Costs:
The advantages of renewable energy extend to our wallets as well. As technology advances and becomes more widespread, the costs associated with renewable energy are decreasing. This trend is expected to continue, making it an economically viable option for many. The renewable energy importance in ensuring affordable energy for all cannot be understated. As prices continue to drop, more and more people will have access to clean, renewable energy.
7. Health Benefits:
The importance of renewable energy is also evident in the health benefits it offers. Traditional fossil fuels release pollutants that can lead to a host of health issues, from respiratory problems to cardiovascular diseases. Around 99 percent of people worldwide breathe air that is polluted and poses a health risk, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO), and more than 13 million people die from preventable environmental causes, such as air pollution, each year. Transitioning to renewable energy can mitigate these health risks. The cleaner the air, the healthier the population, underscoring the need for renewable energy.
8. Diversification of Energy Sources:
The benefits of renewable energy also lie in the diversification of energy sources. Solely relying on one energy source is risky. Renewable energy offers a diversified energy portfolio, ensuring a steady supply even if one source faces challenges. This diversification is crucial for energy security and stability, highlighting the importance of renewable energy sources.
9. Supporting Local Communities:
Community-based renewable energy projects have a direct positive impact on local communities. These projects not only ensure a steady supply of energy but also stimulate local economies by creating jobs. The importance of renewable resources in fostering community development and cohesion is a testament to the multifaceted benefits of renewable energy.
10. Addressing Climate Change:
The importance of renewable energy in addressing climate change is paramount. As global temperatures rise and the effects of climate change become more pronounced, the need for renewable energy becomes more urgent. By reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable energy solutions, we can combat the adverse effects of climate change, ensuring a safer planet for future generations.
By 2030, cheap electricity generated from renewable sources may account for 65 percent of the world’s total electrical production. By 2050, it could decarbonize 90% of the electricity sector, drastically reducing carbon emissions and assisting in the fight against global warming.
In essence, renewable energy is the future. Its myriad advantages, from environmental to economic, present an irrefutable argument for its widespread adoption. As we stand at the crossroads of an energy revolution, the importance of renewable energy sources becomes paramount. The energy sources of the future are here, and they promise a brighter, greener, and more sustainable tomorrow.
5. Conclusions
Renewable energy sources have a combined installed capacity of 150+ GW.
As of Dec 2023, Renewable energy sources, including large hydropower, have a combined installed capacity of 180.79 GW.
The following is the installed capacity for Renewables:
- Wind power: 44.73 GW
- Solar Power: 73.31 GW
- Biomass/Co-generation: 10.2 GW
- Small Hydro Power: 4.98 GW
- Waste To Energy: 0.58 GW
- Large Hydro: 46.88 GW
India has set a target to reduce the carbon intensity of the nation’s economy by less than 45% by the end of the decade, achieve 50 percent cumulative electric power installed by 2030 from renewables, and achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2070. India aims for 500 GW of renewable energy installed capacity by 2030.
References
Books / Renewable energy
Sustainable Energy – without the hot air. David J. C. MacKay, 2008
Renewable Energy: Power for a Sustainable Future 1996
Fundamentals and Applications of Renewable Energy. Yunus A Çengel, 2019
Renewable Energy Resources, John Twidell, 1986
The New Map: Energy, Climate, and the Clash of Nations, Daniel Yergin, 2020
The Renewable Energy Handbook: The Updated Comprehensive Guide to Renewable Energy and Independent Living, William H. Kemp, 2009
Renewable Energy Systems: A Smart Energy Systems Approach to the Choice and Modeling of 100% Renewable Solutions, Henrik Lund, 2014
Renewable Energy Engineering, Nicholas Jenkins, 2017
Solar revolution, Travis Bradford, 2006
Introduction to Renewable Energy, Vaughn Nelson, 2011
The Solar Economy, Hermann Scheer, 2002
Renewable Energy Finance: Theory and Practice, Santosh Raikar, 2019
Textbook of Renewable Energy, S. C. Bhatia, 2018
Renewable Energy: Discover the Fuel of the Future with 20 Projects, Erin Twamley, 2016
Renewable Energy in India: Economics and Market Dynamics, Sushanta K. Chatterjee, 2021



Comments
Post a Comment
"Thank you for seeking advice on your career journey! Our team is dedicated to providing personalized guidance on education and success. Please share your specific questions or concerns, and we'll assist you in navigating the path to a fulfilling and successful career."