B2C: What's It is, How It Works, Why Transformation in Market Taking Place, Skills Needed for Jobs and Emerging Challenges? The Ultimate Guide to Act on Better Strategies!
In a B2C transaction, there are two parties involved:
- The business: This is the company that produces and sells the product or service.
- The consumer: The individual or household purchases the product or service from the business.
The B2C process is the series of steps a business takes to sell its products or services to consumers.
The steps in the B2C process include the following:
1. Marketing: The business creates awareness for its product or service through marketing activities, such as advertising, public relations, and social media.
2. Sales: The business sells its product or service to consumers. This can be done through online channels, such as an e-commerce store, or offline channels such as a brick-and-mortar retail store.
3. Delivery: The business delivers the product or service to the consumer. This can be done electronically, through email or download, or physically through shipping.
4. Customer service: The business provides customer service to the consumer. This can include answering questions, resolving issues, and providing refunds or returns.
Direct Sellers
Direct sellers — sometimes referred to as direct-to-consumer (DTC) sellers — are the most common online B2C business model and rely on customers making online sales directly from the seller.
These are the online retailers that sell products either from their own brand or various alternative brands.
B2C Dropshipping.
With B2C dropshipping, businesses do not have to hold inventory and only place product orders as they come in from customers. This means no packaging, shipping or storage costs as they fall on the supplier instead.
For online retailers, wholesalers and small businesses, dropshipping can be a beneficial business solution as it can lead to significant profits while cutting down on extraneous costs.
Online Intermediaries.
Online intermediaries act as the link between buyers and sellers. They do not own products, services or brands — their job is to provide a platform for the buyers and sellers to trade.
Larger companies that act as online intermediates include Etsy and Expedia.
Community-based.
With a community-based ecommerce platform, businesses leverage online forums and communities with a large user base related to the products and services they wish to sell.
By using these platforms, businesses can take advantage of a pre-existing space to promote and raise awareness of their ecommerce capabilities.
Fee-based.
A fee-based ecommerce model charges customers via subscription in exchange for using their websites and unrestricted access to their content.
In the online world, this is an increasingly common B2C business model. Companies that use it include Netflix, Amazon Prime and Hulu.
Advertisement-based.
Advertisement-based B2C ecommerce do not own any products or services. They help sellers to put out news about their business by creating traffic around online content.
- Cultural differences
- Language barriers
- Logistics and infrastructure
- Legal barriers
- Payment methods
- Local competitors
Cultural Differences:
Understanding different cultures is a vital part in international businesses. Suppose the meaning of the product name is different in the source country and the target country. The potential consumer won’t be able to understand what the company is offering. Also certain customs and preferences change in different regions of the same country.
Language Barriers:
It can be a huge drawback for the businesses if they do not understand the language of the other country where they want to enter. If the consumers do not understand what the product offers there is no chance of making sales in that particular country.
Logistics and Infrastructure:
Setting up logistics and infrastructure could be a challenge to B2C commerce businesses while expanding to foreign countries. This includes setting up warehousing, transportation, and delivery networks. These elements must be cost-effective otherwise they can lead to losses or a decline in profits.
Legal Barriers:
It is extremely important to keep the local laws in consideration, because a single mistake can cease your business to operate in that country. All the business documents must be done with precise manner in the local language.
Payment Methods:
B2C e-commerce businesses must ensure they can process payments securely and efficiently in foreign countries. Because payment methods vary from country to country.
Local Competitors:
B2C commerce businesses will definitely face fierce competition from local businesses and established global players. They must be able to differentiate themselves from others by adopting unique traits in their brand.
7. What Are B2C solutions for the challenged in eCommerce?
Solutions to the challenges of B2C eCommerce
- Cultural awareness
- Language training
- Logistics and infrastructure solutions
- Legal knowledge
- Payment solution
- Unique competitive measures
Cultural Awareness:
All the employees in B2C companies must be fully aware of the local culture of the target consumers and for that the companies can provide cultural training to their employees. But for a medium and small companies training their employees can be expensive. In that case they can hire any other company who solely deals in the area of localization.
Products/Services Translation:
Brands need to make sure that they advertise their product and services in the local language. Translating business content must be done in all the languages majorly spoken in the country. This could be done with the help of localization as localization involves adapting products, marketing materials, and other content to the local language and culture. Translation agencies can be helpful in this case.
Logistics and Infrastructure Solutions:
Instead of setting up their own warehouses and delivery methods, B2C commerce businesses can work with local logistics providers to optimize their warehousing, transportation, and delivery networks. This can prove cost-effective and help them gain a competitive edge in foreign markets.
Legal Knowledge:
B2C businesses can seek help from local legal experts to avoid any hurdles in the smooth flow of the businesses.
Payment Solution:
With the help of local payment methods used by the majority, B2C brands can improve payment processing efficiency and reduce payment fraud.
Unique Competitive Measures:
B2C commerce businesses can tackle the competition by adapting attractive ways of marketing their products, providing great customer support, and of course, the best product.
The following are some of the top advantages of B2C eCommerce:
1. The inflexibility of the catalog
The direct “link” has the potential to display content data and other visual elements that are already prevalent on websites owned by a variety of clients. You no need to beg the marketing consultancy agency.
2. Shrinks Competition Gap
The low cost of marketing and advertising creates opportunities for us to compete with well-known enterprises in terms of the cost, quality, and accessibility of the items.
3. Unlimited Market Place
By allowing customers to browse and shop at their convenience, it displays an unlimited market. Online stores no longer need a marketing consultancy agency.
4. 24-Hour Store with a Shorter Sale Cycle
There is no need to send lengthy emails or place an excessive number of phone calls.
5. Lower Cost of Business
The B2C model has decreased the cost of doing business across a range of areas, including hiring staff, purchasing expenses, mailing confirmations, telephone conversations, clerical work, and the need to open physical locations.
6. Eliminating Third Party Clients
We are free to sell our items straight to clients without engaging any third parties in the transaction.
7. Business Administration Made Simpler
Compared to the conventional methods of business administration, it has become simpler to record store inventories, shipments, logs, and all other.
The following are some of the top disadvantages of B2C eCommerce:
1. Lack of Catalog Flexibility
However, it’s crucial to rearrange the catalog after adding new data and merchandise correspondingly.
2. Infrastructure
Even though it has a huge customer reach and overcomes cultural boundaries by addressing everyone on the same channel, the truth still stands.
3. Competition
Since there are thousands of online stores and services, the rivalry is indeed fierce and could jeopardize our company’s consumer base. Some online stores have been able to keep a sizable portion of the market, allowing them an opportunity to endure over time.
4. Product Exposure Limits
It is important to note that e-commerce has limited the amount of product exposure available to purchasers online, although it provides them with easy accessibility and a special degree of product customization.
5. Entering a Cut-Throat Competition
Without conducting market research and B2C Campaigns, many people are influenced to launch a B2C e-commerce business. As a result, they begin to cater to the market or special segment where numerous e-commerce companies are already created to serve the public.
6. Shipping Charges
Whether you sell in large or small quantities, transportation fees are a reality. Additionally, clients demand free shipping in the modern e-commerce industry.
7. Security Concerns
The transactional data from your site can be hacked by a lot of cybercriminals. After that, they are free to use someone else’s name to purchase anything they want.
B2C marketing is all about understanding customer needs and tailoring your online approach to suit those requirements. Here are just some of the ways that you can make the most of your B2C marketing plan with some careful preparation and focus.
1. Focus on building brand loyalty
Once you’ve taken some time to figure out who your prospects are and what they’re looking for from you, your focus should be on developing strong brand loyalty. The easiest way to do this is often with B2C marketing companies who can help you to figure out how to speak to your target audience. Often, developing loyalty means segmenting your audience so that you can offer each group the exact experience they’re looking for. You can also think about building VIP and loyalty campaigns for your most valuable customers.
2. Use influencers to boost social proof
We mentioned the value of social proof in B2C marketing above. Your customers want to know they can rely on you to deliver a great product or service, and one great way to convince them. This can be done with influencer marketing, you can use an industry leader or celebrity’s power in a specific niche to turbo-charge your campaigns. The great news? You don’t even need to use a high-profile celeb. Instead, a micro-influencer with a good following could be a great way to enhance both B2B and B2C marketing strategies.
3. Help customers understand your brand
As clients become pickier about who they do business with, it’s important for B2C marketing teams to be strategic about the way they promote brands. Today’s customers, especially in the millennial demographic, want to feel as though they’re working with brands that have a positive impact on the world. Anything that helps your customer resonate with your company is valuable.
4. Use multiple channels at once
The more you learn about B2C marketing, the more you’ll discover that your customers can come to you through a selection of different avenues. While some will find you through your thought-leadership posts and guides, others will come to you through links on your social media channels or press releases. It’s a good idea to employ multiple channels to engage your customers and reach out to new clients. For instance, you could:
- Host in-person events.
- Have an email compaign
- Use newsletters.
- Write blogs and articles.
- Use podcasts
- Share messages on social media.
5. Constantly assess and improve
Periodic assessment of your B2C marketing strategies is an excellent way to make sure that you’re on the right track when reaching out to your consumers. The parameters that you’ll need to measure will depend on the unique goals of your campaign, but just some of the metrics that most organisations track include:
- Sales volumes linked to content marketing campaigns.
- Return on investment for advertising strategies.
- Customer response and engagement.
- Create brand awareness (shown in social media followers, website traffic etc).
- Competitor response.
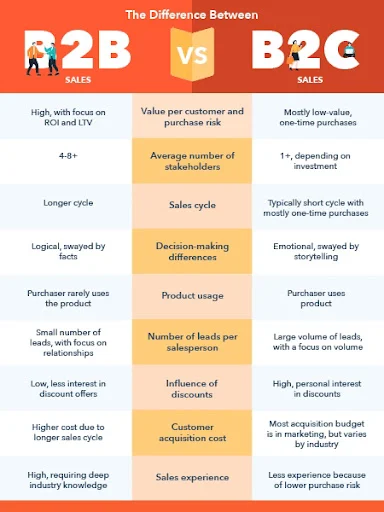
Differences Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | B2B | B2C |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The selling of goods and services between two business entities is known as Business to Business or B2B. | The transaction in which business sells the goods and services to the consumer is called Business to Consumer or B2C. |
| Customer | Company | End user |
| Focus on | Relationship | Product |
| Quantity of merchandise | Large | Small |
| Relationship | Supplier - Manufacturer Manufacturer - Wholesaler Wholesaler - Retailer | Retailer - Consumer |
| Relationship horizon | Long term | Short term |
| Buying and Selling cycle | Lengthy | Short |
| Buying Decision | Planned and Logical, based on needs. | Emotional, based on want and desire. |
| Creation of Brand Value | Trust and Mutual Relationship | Advertising and Promotion |
B2C marketing serves the customers and addresses their concerns within various products and services.
One thing to note here is that customers look out for goods and services to meet their needs. With the help of b2c purchases, users typically complete their purchase within a few hours or days after knowing about the brand offerings.
To complete the sales process quickly, the businesses give a lot of time to research and understand the customers' buying habits, market trends, and strategies and methods to implement for closure.






Comments
Post a Comment
"Thank you for seeking advice on your career journey! Our team is dedicated to providing personalized guidance on education and success. Please share your specific questions or concerns, and we'll assist you in navigating the path to a fulfilling and successful career."